Table Of Content
What Is an Ethereum Wallet and How Does It Work?
An Ethereum wallet is a digital tool for storing, sending, and receiving ETH (Ether) and interacting with Ethereum-based applications like DeFi platforms, NFTs, and smart contracts.
Unlike traditional wallets that hold physical cash, Ethereum wallets manage private keys that prove ownership of ETH and allow transactions on the blockchain.
These wallets come in various forms—web, mobile, desktop, hardware, and browser extensions—each offering different levels of security, accessibility, and control.
Choosing the right Ethereum wallet depends on how you plan to use ETH, your security preferences, and how often you interact with dApps.
-
How Ethereum Wallets Work
Ethereum wallets don’t store ETH directly. Instead, they store private keys that grant access to your ETH on the blockchain. Here's how they function:
Private and Public Keys: Your Ethereum wallet generates a pair of keys. The public key creates your wallet address, and the private key authorizes transactions.
Sending ETH: To send ETH, you input the recipient’s address, amount, and sign the transaction using your private key. This is broadcast to the Ethereum network for confirmation.
Interacting with dApps: Wallets like MetaMask let you connect to DeFi platforms or NFT marketplaces, enabling seamless interaction with smart contracts.
Because Ethereum is programmable, wallets are more than just storage—they’re gateways to the decentralized web.
Ethereum Wallets: Pros and Cons
Ethereum wallets offer flexibility, control, and access to decentralized apps—but they also come with risks that depend on wallet type and usage.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Full Control Over Funds | Loss of Private Key = Loss of Funds |
Access to dApps and NFTs | Susceptibility to Scams or Phishing |
Versatile Asset Support | Network Fees (Gas Costs) |
Global, Permissionless Use | Complexity for Beginners |
- Full Control Over Funds
Non-custodial Ethereum wallets give you complete ownership—no middleman needed to move or manage your ETH.
- Access to dApps and NFTs
Web3 wallets like MetaMask allow direct connection to DeFi platforms, staking services, and NFT marketplaces.
- Versatile Asset Support
Ethereum wallets support not only ETH but also ERC-20 tokens (like USDT or UNI) and NFTs (ERC-721, ERC-1155).
- Global, Permissionless Use
Anyone with an internet connection can use an Ethereum wallet to send money or participate in DeFi.
- Loss of Private Key = Loss of Funds
If you forget your recovery phrase or lose your private key, there’s no way to retrieve your assets.
- Susceptibility to Scams or Phishing
Especially with browser-based or mobile wallets, users are vulnerable to fake websites or malicious dApps.
- Network Fees (Gas Costs)
Transactions require ETH to cover gas fees, which can spike based on network congestion.
- Complexity for Beginners
Wallet setup, seed phrase storage, and gas settings can be confusing for new users.
Key Things You Can Do with an Ethereum Wallet
An Ethereum wallet is more than just a storage tool—it enables users to actively participate in the growing Ethereum ecosystem.
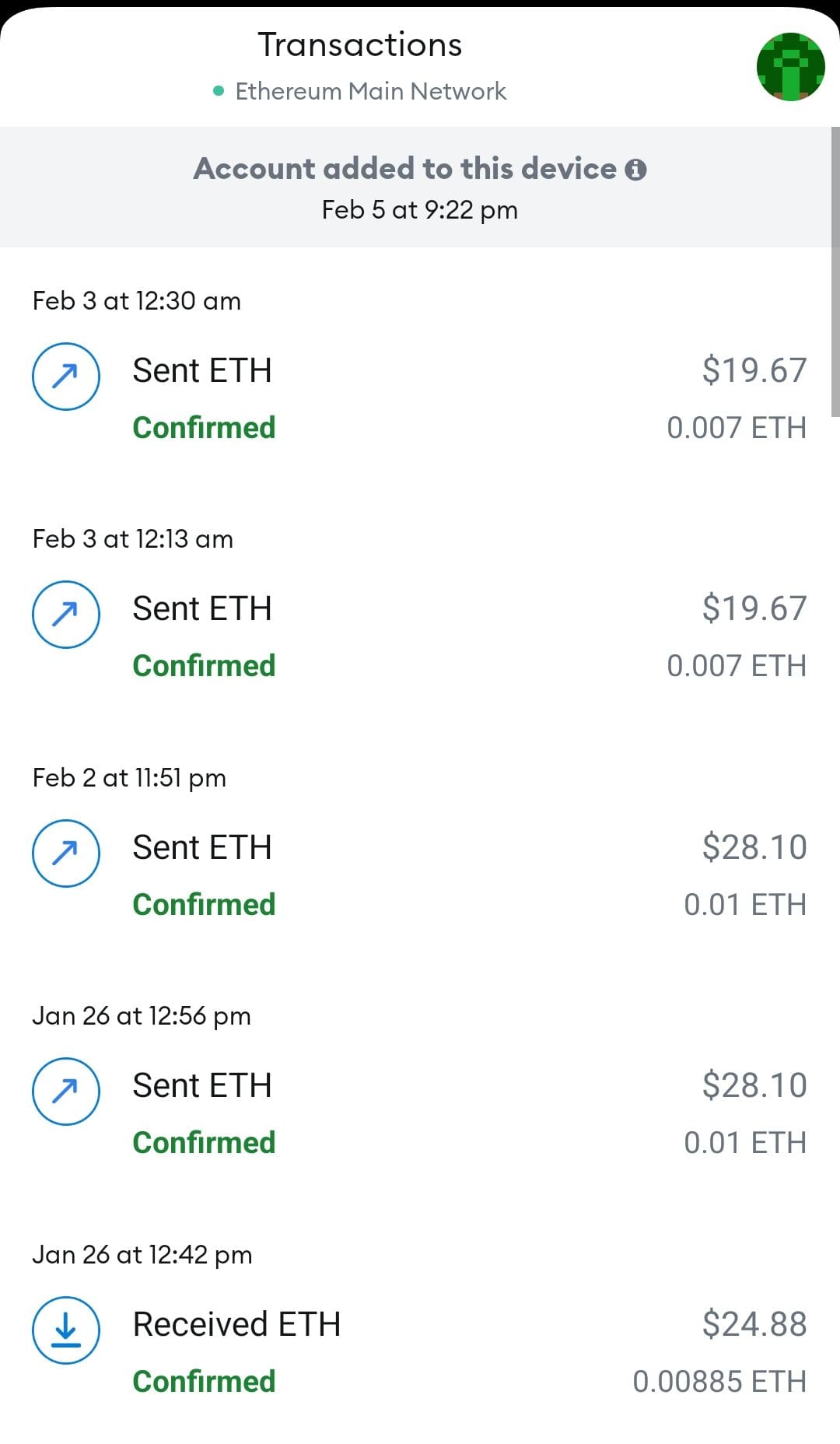
Send and Receive ETH: You can transfer ETH to friends, pay for services, or receive payments from others by using your wallet address.
Store and Swap Tokens: Ethereum wallets support ERC-20 tokens like USDC or LINK, and many let you swap them directly within the app.
Connect to DeFi Platforms: Wallets like MetaMask allow you to lend, borrow, or stake assets on platforms like Aave, Compound, or Uniswap.
Access NFT Marketplaces: You can mint, buy, sell, or hold NFTs through integrations with OpenSea, Rarible, and other NFT platforms.
Stake ETH for Rewards: Many wallets support ETH staking through platforms like Lido or via native validator staking for passive income opportunities.

Types of Ethereum Wallets: Hot vs. Cold Storage
Ethereum wallets fall into two main categories: hot wallets and cold wallets, each with distinct advantages depending on how you use and store ETH.
- Hot wallets are internet-connected and great for frequent transactions or accessing DeFi apps.
- Cold wallets store your private keys offline, making them ideal for long-term security.
Because security and convenience vary, many investors use both types—keeping most ETH in cold storage while using hot wallets for day-to-day activity.
Feature | Hot Wallet | Cold Wallet |
|---|---|---|
Connection | Always online | Offline storage |
Security Risk | Higher (vulnerable to hacks/phishing) | Very low if properly stored |
Convenience | Easy access for dApps & NFTs | Requires extra steps to access funds |
Best For | Active users, DeFi, small balances | Long-term holders, large balances |
Examples | MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet | Ledger Nano, Trezor Model T |
How to Transfer ETH to an Ethereum Wallet
Transferring ETH to your Ethereum wallet is simple, but accuracy is key.
Install and Set Up Wallet: Download a reputable wallet (e.g., MetaMask or Trust Wallet) and safely store the 12- or 24-word recovery phrase.
Copy Your ETH Address: On the wallet’s main screen, tap or click to copy your Ethereum address (starts with “0x…”).
Send ETH from Exchange: Log into your crypto exchange, paste the wallet address, and initiate the transfer. Consider sending a small test amount first.
Confirm on Blockchain: Use Etherscan to verify the transaction status using your wallet address or transaction hash.
Avoid copying addresses from memory—always double-check before confirming.
Popular Wallets for Ethereum
Choosing the right Ethereum wallet depends on how you plan to interact with the Ethereum ecosystem. Below are some widely used options.
MetaMask: A browser and mobile wallet that supports all Ethereum-based assets and easily connects to DeFi platforms and NFT marketplaces.
Trust Wallet: A mobile-first, beginner-friendly wallet with support for ETH, ERC-20 tokens, and in-app staking and swaps.
Ledger Nano X: A hardware wallet offering secure offline storage for ETH and other crypto, compatible with Web3 apps via Ledger Live or MetaMask.
Trezor Model T: Another leading hardware wallet with touchscreen navigation and strong security features for ETH holders.
Each offers different strengths in security, ease of use, or ecosystem access—so it’s worth comparing them before committing.
FAQ
Yes, you can use as many Ethereum wallets as you’d like. Many users separate wallets for staking, NFTs, and general trading to better organize funds and manage risk.
If it's a non-custodial wallet and you lose your recovery phrase, your funds are permanently inaccessible. Custodial wallets may allow recovery through customer support.
No, a wallet gives you control over your private keys, while an exchange stores your crypto for you. Wallets are better for long-term security and decentralization.
Yes, Ethereum wallets can store ETH and Ethereum-based tokens such as ERC-20, ERC-721 (NFTs), and ERC-1155 assets, depending on the wallet's features.
Most Ethereum wallets do not support Bitcoin or non-EVM chains unless they're multi-chain wallets like Trust Wallet or Atomic Wallet.
Yes, if you restore it using your recovery phrase. However, you must do so carefully and ensure your devices are secure to prevent unauthorized access.
They offer pseudonymity. Wallets don’t require ID, but transactions are publicly visible on the blockchain and can sometimes be linked to individuals through exchanges or metadata.
Write down your 12–24 word recovery phrase and store it securely offline. Do not store it on cloud services or in emails to avoid hacks.
Yes, through staking platforms or DeFi apps. Some wallets integrate with protocols like Aave or Lido to help you earn yield on ETH or stablecoins.
