Table Of Content
What Is Short Selling in Crypto?
Short selling in crypto is a trading strategy where investors bet that a cryptocurrency’s price will drop.
Instead of buying low and selling high, traders borrow coins at a higher price, sell them on the open market, and later buy them back at a lower price to return to the lender—profiting from the difference.
It’s often used in volatile markets or during bearish trends, but also carries higher risk due to potential price surges.
Shorting is typically done via margin trading or derivatives on platforms like Binance, Kraken, and Bybit.
How to Short Sell Cryptos on Major Exchanges
Short selling crypto involves a few key steps—starting with selecting a trading platform and enabling margin or derivatives trading.
1. Choose a Reputable Exchange That Supports Shorting
Before short selling, you’ll need to find a platform that allows margin trading or futures contracts, such as Binance, Kraken, or Bybit.
Binance Futures and Margin: Binance offers futures and margin trading with up to 10x leverage on selected crypto assets.
Kraken Margin Trading: With a regulated interface, Kraken supports up to 5x leverage for major coins like BTC and ETH.
Bybit for Derivatives: Bybit is known for derivatives and perpetual contracts, making it ideal for short-selling strategies.
Choose a platform based on fees, liquidity, leverage limits, and available trading pairs. Always review terms and risks before proceeding.
Exchange | Shorting Method | Max Leverage | User-Friendliness |
|---|---|---|---|
Binance | Margin & Futures | Up to 125x | Moderate |
Kraken | Margin Trading | Up to 5x | High |
Bybit | Perpetual Futures | Up to 100x | High |
OKX | Futures & Perpetuals | Up to 75x | Moderate |
2. Enable Margin or Derivatives Trading on Your Account
Most platforms require users to activate margin or futures trading separately due to the added risk.
Complete KYC Verification: Exchanges like Kraken and Binance require full identity verification before granting access to leveraged products.
Accept Margin Terms: You must agree to the margin trading terms, which outline risks like liquidation and interest fees.
Transfer Funds to Margin Wallet: Move USDT, BTC, or other supported assets to your margin or derivatives wallet.
Margin and futures enable you to trade with borrowed capital—but if your position moves against you, losses can exceed your initial investment.
Aspect | Margin Trading | Futures Trading |
|---|---|---|
Ownership of Asset | Yes (borrowed) | No (contract-based) |
Settlement | Immediate | Set date or perpetual |
Complexity | Moderate | Higher |
Risk of Liquidation | High | Very High (especially with leverage >10x) |
Ideal for | Short-term traders, small positions | Experienced traders, high-leverage strategies |
- The Smart Investor Tip
Before funding your margin account, use a Position Size Calculator to understand how much you can risk without overleveraging.
Make sure you review margin interest rates—they vary by coin and can eat into profits over time.
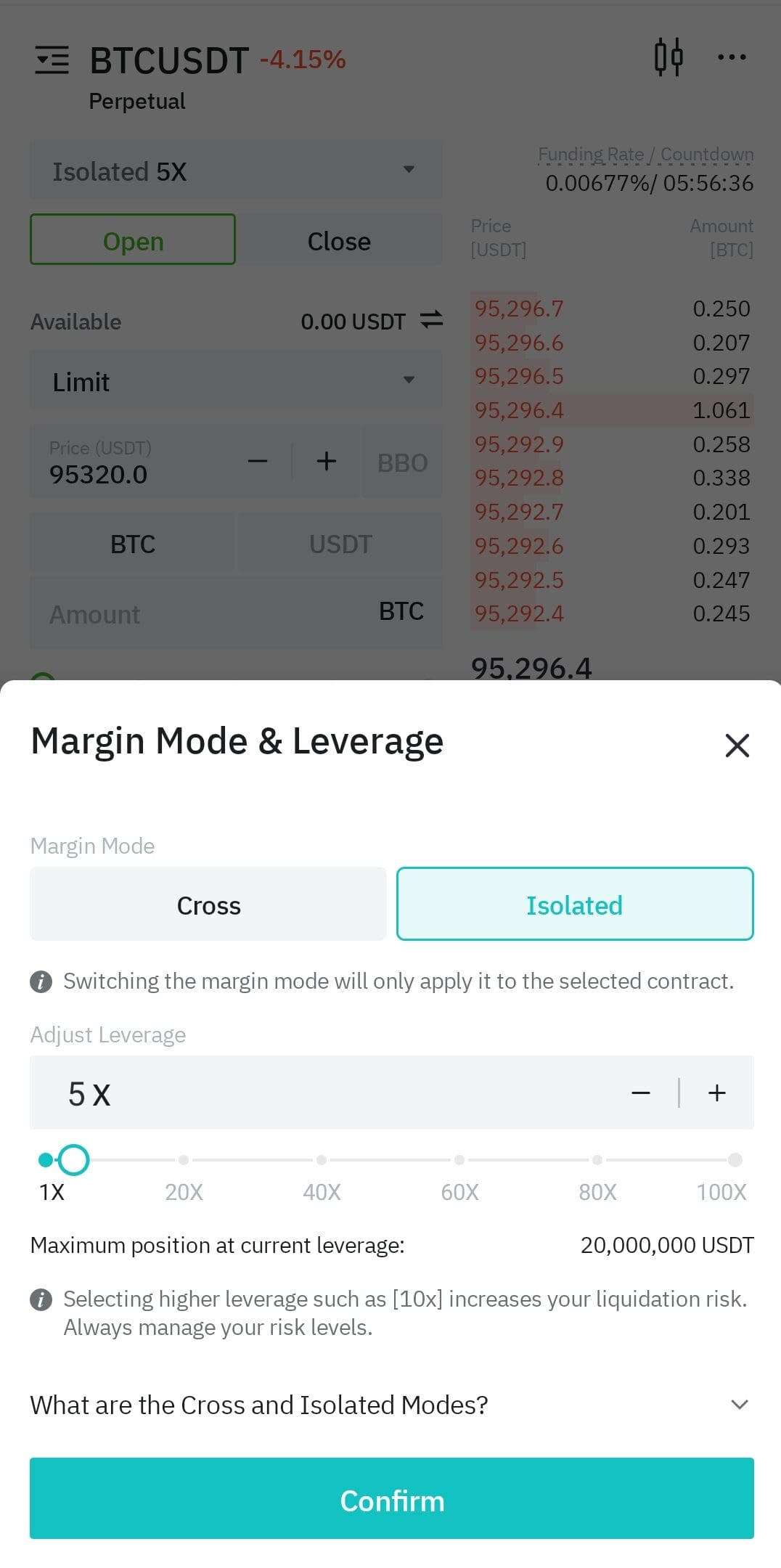
3. Open a Short Position on the Selected Crypto
Once your account is funded and margin enabled, you can execute a short position by borrowing and selling the coin.
Borrow the Asset: You borrow the crypto (e.g., 1 BTC) from the exchange using margin.
Sell Immediately at Market Price: The borrowed crypto is sold at the current market price to capture potential downside.
Set Short Trade Parameters: Choose your entry point, leverage, and stop-loss to manage downside risk.
The goal is to repurchase the same asset later at a lower price. Timing is critical, so monitor technical indicators and market sentiment.
4. Monitor and Manage the Short Trade Actively
Because of the volatility in crypto, active management of short positions is essential to avoid liquidation.
Watch Liquidation Price: Exchanges display the liquidation threshold—if the price hits it, your position is closed automatically.
Adjust Stop-Loss or Take-Profit: Lock in gains or limit losses by modifying your stop orders as the market shifts.
Check Funding Rates: In perpetual futures, you may pay or receive fees depending on long vs. short demand.
Crypto prices can swing rapidly due to news or social media, so stay updated and use trailing stop-loss strategies if supported.
- The Smart Investor Tip
Don’t “set and forget”—crypto markets run 24/7, so consider using a mobile trading app with alerts to track key price levels or liquidation thresholds in real time.
5. Close the Short and Repay the Loan
Once the price drops to your target level, it’s time to buy back the asset and finalize the trade.
Buy Back the Crypto: Repurchase the borrowed coins at a lower price, securing your profit.
Repay the Margin Loan: Return the borrowed amount to the exchange, plus any accrued interest.
Review Trade Summary: Check profit/loss, fees paid, and total margin used to evaluate trade performance.
Successfully closing the short locks in your gains—but if the market went up instead, you may face losses or forced liquidation. Always analyze post-trade results to refine your strategy.
How to Use Crypto Futures for Short Selling?
Crypto futures are derivative contracts that allow traders to speculate on the future price of cryptocurrencies without owning the underlying asset.
These contracts are settled at a later date and are available on exchanges like Binance Futures, Bybit, and OKX. To short using crypto futures:
Open a Futures Account: Enable futures trading on your exchange and fund it with USDT or another supported asset.
Select the Trading Pair: Choose a futures contract like BTC/USDT Perpetual and analyze the price trend.
Place a Short Order: Enter a sell order to open a short position. If the coin’s price drops, you earn the difference.
Manage the Position: Use stop-loss, take-profit, and monitor funding rates to control risk.
Futures offer leverage, but also come with liquidation risk, so managing exposure is crucial.
Best Crypto Short Selling Indicators
These indicators can help traders identify potential downtrends in crypto markets and time their short positions more effectively.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): An overbought reading (above 70) can signal a possible downward reversal.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): A bearish crossover often indicates momentum is shifting toward sellers.
Volume Spikes with Price Drops: High volume during declines may confirm strong selling pressure.
Bearish Candlestick Patterns: Patterns like evening stars or shooting stars can signal upcoming reversals.
Funding Rate Flips Negative: In futures, a negative funding rate shows short sellers are dominant.
These indicators work best when combined for confirmation. For example, pairing RSI with MACD can reduce false signals and improve timing.
Short Selling in Crypto: Benefits & Risks
Short selling offers unique opportunities in crypto markets but also carries major risks, especially in fast-moving or unpredictable conditions.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Profit from falling prices | Unlimited potential losses |
Hedge against long positions | Margin calls/liquidations possible |
Use of leverage to amplify gains | Complex for beginners |
Broad platform availability | Requires constant monitoring |
- Profit from Declines
Traders can earn money during market crashes or bearish trends, offering portfolio diversification.
- Hedge Long Positions
Shorting helps offset potential losses in spot holdings during downtrends or corrections.
- High Liquidity on Major Platforms
Exchanges like Binance and Bybit offer liquid futures and margin markets for many assets.
- Leverage Increases Capital Efficiency
You can control large positions with less capital—but it should be used cautiously.
- Unlimited Loss Potential
If the price rises instead, losses can grow quickly beyond your initial margin.
- Forced Liquidation Risk
Sudden price spikes can trigger margin calls or auto-liquidation.
- Complex Strategy for Beginners
Requires advanced knowledge of risk, indicators, and trading mechanics.
- Funding Fees and Costs
Holding short futures can incur ongoing fees, reducing profits over time.
FAQ
Not all coins are available for shorting. Most platforms limit this feature to highly liquid assets like BTC, ETH, and a few large-cap altcoins.
Yes, short selling is legal in most jurisdictions as long as the platform offering it complies with local regulations. However, some regions restrict margin trading.
You can short with smaller capital amounts using leverage, but this increases risk significantly. It's essential to manage position size wisely.
It's uncommon, but some platforms allow short positions without leverage using inverse ETFs or tokenized products. Most short selling, however, involves borrowing or leverage.
If the price rises, your losses grow and could lead to liquidation if your collateral falls below the platform’s margin requirements.
Shorting is more suited for experienced traders due to its risk and complexity. Beginners should practice with demo accounts or smaller positions first.
There’s no strict limit on futures, but in margin trading, you may pay daily interest fees. Always check platform rules for loan duration.
You typically pay interest on borrowed assets and may owe funding fees if the futures funding rate is negative for short positions.
Yes, profits from short selling are usually considered taxable events. Consult a tax professional familiar with crypto regulations in your country.
